Gallium was discovered in 1971. It is a non-radioactive, non-toxic metal and have been widely used a semiconductors in various electronic devices.
History and Discovery
Dmitri Mendeleev predicted the existence of gallium in 1971 and named it eka-aluminum. He also predicted some properties of gallium which were later confirmed when the element was discovered [1]. In 1875, Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran a French chemist discovered gallium through spectroscopically analysis of sphalerite and observing violet lines in spectrum [2]. The element was named gallium after the Latin word Gallia that was the native land of French discoverer.
Atomic Data for Gallium (Ga) Atomic Number = 31 Atomic Weight = 69.723 Reference E95: Isotope: Mass: Abundance: Spin: Mag Moment: 69 Ga: 68.925580: 60.11%.

Gallium
- Gallium is also extracted from the flue dusts of coal. Isotopes: Gallium has 24 isotopes whose half-lives are known, with mass numbers 61 to 84. Of these, two are stable: 69 Ga and 71 Ga with natural abundances of 60.1% and 39.9% respectively.
- The gram atomic mass for gallium is 69.72. 'Mass number' is a property of isotopes, not of elements, and gallium has two radioactively stable isotopes, with mass numbers of 69 and 71.
- Effective mass of density of state m v: 1.5 m 0: Leszczynski et al. (1996), Fan et al. (1996) Effective electron mass m e: 0.20 m o: 300 K: Bougrov et al. (2001) 0.27 (6) m o: 300K; Faraday rotation: Rheinlander & Neumann: Effective electron mass m e: 0.20(2) m o: 300K; fit of reflectance spectrum: Bloom et al.(1973) Effective electron mass.
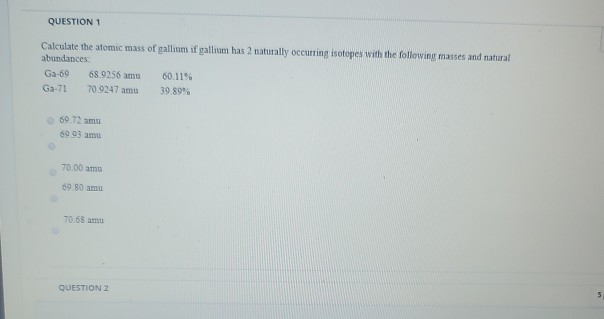
- To determine the atomic mass of gallium in the newly discovered planet, we should take into account the presence of both isotopes (Ga-69 and Ga-71) and their relative abundances on the location.
| Periodic Table Classification | Group 13 Period 4 |
|---|---|
| State at 20C | Solid |
| Color | Silvery blue |
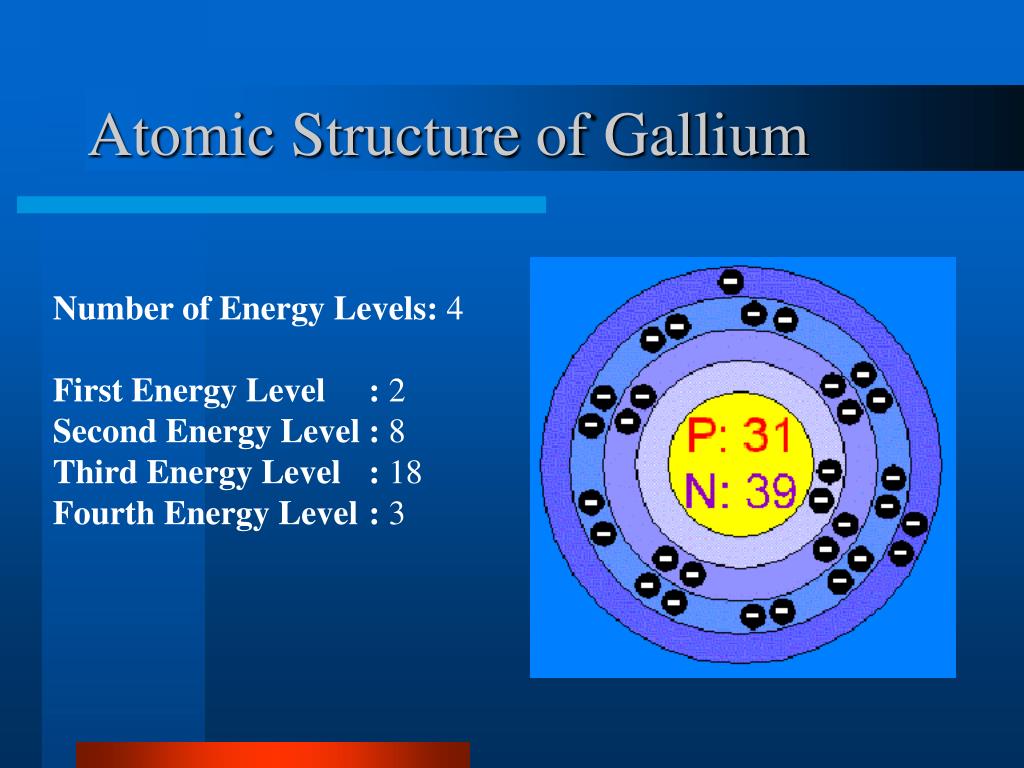
| Electron Configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p1 |
| Electron Number | 31 |
| Proton Number | 31 |
| Electron Shell | 2, 8, 18, 3 |
| Density | 5.91 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Atomic number | 31 |
| Atomic Mass | 69.72 g.mol -1 |
| Electronegativity according to Pauling | 1.81 |
Occurrence
Gallium is a not an abundant element and is present in about 16.9ppm in the Earth’s crust. It Gallium does not exist in elemental form in nature. Gallium is also found in scarce amount in minerals such as gallite [3]. It is mainly present in the ores of aluminum (bauxite) and zinc. Commercially, gallium is produced through smelting of various ores, including bauxite and some ores of zinc sulfide.
Physical Characteristics
Gallium is bluish silver metal. It is soft at STP (standard temperature and pressure), while at low temperature, it acquires a brittle solid state. Gallium also exists in liquid form at temperature more than 29.76 °C. When gallium is held in the hand, it melts and is re-solidified when placed back from hand. Thus, the melting point of gallium is 29.76 °C. Melting point of gallium is used as reference point of temperature set by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). The boiling point of gallium is also unique, as it is the only element that has the greatest difference or ratio between boiling and melting point as the boiling point is 2399°C which is about eight times higher than its melting point. At high temperature, gallium has a low vapor pressure. Gallium belongs to the boron group (Group 13) along with aluminum, indium, thallium and nihonium. When gallium is frozen, it expands as it solidifies, so care should be taken while storing gallium at low temperatures. In solid form, it forms an orthorhombic crystal shape with eight atoms that form a unit cell. Gallium also tends to supercool below its freezing point into gallium nanoparticles. Gallium is a high-density liquid.
Chemical Characteristics

Gallium is not a very reactive metal. the most common oxidation state of gallium is +3. Gallium dissolves in strong acids and alkalis. Gallium dissolves in water and aqueous solutions of gallium have hydrated gallium ions. Gallium hydroxide is an amphoteric compound and it can dissolve in alkalis and produce salts of gallium. Gallium reacts with ammonia to form gallium nitride at high temperature. It can also react with antimony, arsenic, and phosphorus to form binary compounds. Gallium reacts with halides, including fluorine, chlorine and iodine to form stable compounds. Gallium does not react with water and air at room temperature due to the formation of a surface layer of oxide. However, at higher temperatures, gallium reacts with air to form gallium oxide.
Significance and Uses
- Gallium is widely used in electronic industry. It is part of infrared circuits, microwaves and efficient switching circuits.
- Gallium is used as a non-toxic alternative to mercury in thermometers.
- Gallium is widely used to make alloys that have low melting points.
- Gallium is used in the manufacturing of semiconductors. Gallium nitride semiconductors produce violet and blue light-emitting diodes and lasers.
- Gallium is used to make high quality jewellery, for instance gadolinium gallium stones that have brilliant looks that resembles diamonds or gemstones.
Health Hazards

Gallium is not a biologically significant element. It is a non-toxic element. Gallium is also a non-radioactive metal.
Isotopes of Gallium
There are thirty-one isotopes of gallium and their atomic mass range from 56 to 86. The stable isotopes are only two, gallium-69 and gallium-71. The most abundant isotope is gallium-69 and makes around 71% in abundance. All other isotopes of gallium are unstable and radioactive. Gallium-67 and gallium-68 are the commercially important radioactive isotopes of gallium. The lighter isotopes (below gallium-69) decay through emission of positron termed as beta plus emission while the heavier isotopes undergo electron emission that is termed as beta minus decay.
REFERENCES
[1]. Ball, Philip (2002). The Ingredients: A Guided Tour of the Elements. Oxford University Press. p. 105. ISBN978-0-19-284100-1
[2]. de Boisbaudran, Lecoq (1835–1965). “Caractères chimiques et spectroscopiques d’un nouveau métal, le gallium, découvert dans une blende de la mine de Pierrefitte, vallée d’Argelès (Pyrénées)”. Comptes Rendus. 81: 493. Retrieved 2008-09-23.
[3].“The distribution of gallium, germanium and indium in conventional and non-conventional resources – Implications for global availability (PDF Download Available)”. ResearchGate. doi:10.13140/rg.2.2.20956.18564. Retrieved 2017-06-02
Other Periodic Table Elements
- Copernicium
Copernicium is an artificially produced element and was synthesized in 1996. It has many unstable…
- Terbium
Terbium was discovered in 1843. It is stable in the air but very reactive in…
- Gadolinium
Gadolinium was discovered in 1880 and isolated in 1886. It becomes a superconductor at a…
Molar mass of Ga2O3 = 187.4442 g/mol
This compound is also known as Gallium(III) Oxide.
Convert grams Ga2O3 to moles or moles Ga2O3 to grams
Molecular weight calculation:
69.723*2 + 15.9994*3
| Symbol | # of Atoms | Gallium | Ga | 69.723 | 2 | 74.393% | |
| Oxygen | O | 15.9994 | 3 | 25.607% |
In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all of these products together.
Formula weights are especially useful in determining the relative weights of reagents and products in a chemical reaction. These relative weights computed from the chemical equation are sometimes called equation weights.
Finding molar mass starts with units of grams per mole (g/mol). When calculating molecular weight of a chemical compound, it tells us how many grams are in one mole of that substance. The formula weight is simply the weight in atomic mass units of all the atoms in a given formula.
A common request on this site is to convert grams to moles. To complete this calculation, you have to know what substance you are trying to convert. The reason is that the molar mass of the substance affects the conversion. This site explains how to find molar mass.
Atomic Mass Of Gallium-71
If the formula used in calculating molar mass is the molecular formula, the formula weight computed is the molecular weight. The percentage by weight of any atom or group of atoms in a compound can be computed by dividing the total weight of the atom (or group of atoms) in the formula by the formula weight and multiplying by 100.
The atomic weights used on this site come from NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology. We use the most common isotopes. This is how to calculate molar mass (average molecular weight), which is based on isotropically weighted averages. This is not the same as molecular mass, which is the mass of a single molecule of well-defined isotopes. For bulk stoichiometric calculations, we are usually determining molar mass, which may also be called standard atomic weight or average atomic mass.
Atomic Mass Of Gallium Is 69.723 Amu
Using the chemical formula of the compound and the periodic table of elements, we can add up the atomic weights and calculate molecular weight of the substance.
